When you shop for a travel eSIM or glance at your phone’s status bar, you will often see your phone show network types like “LTE”, “4G”, or sometimes even “5G”. Most people just assume it means “fast internet” and move on – which is fair enough, but there’s a bit more to it than that. […]
What is Wi-Fi Assist? How to turn on/off on iPhone
Wi-Fi Assist is a feature on iOS devices designed to enhance your mobile internet experience by seamlessly switching between WiFi and cellular data.

Picture this: You are on a video call for an important work meeting, walking from your home office to the kitchen. When you move, your WiFi signal fades. Typically, this might cause your call to drop or freeze. However, if Wi-Fi Assist is turned on, your phone can automatically switch to cellular data, thereby keeping your conversation flowing without a hitch.
This example highlights the importance of Wi-Fi Assist in maintaining smooth experience, which can be crucial in today’s communications. This article will explain “What is Wi-Fi Assist?“, how to turn on/off this feature on an iPhone and use it properly.
In this article
I. What is Wi-Fi Assist?
WiFi Assist is an intelligent network management feature introduced by Apple for iOS devices. It automatically detects when your WiFi connection is poor and replaces it with cellular data to maintain a stable internet connection.
This transition happens seamlessly in the background, ensuring that your online activities continue without interruption.
II. Which devices support Wi-Fi Assist?
Wi-Fi Assist works with most apps such as Safari, Apple Music, Mail, Maps, and others.
It is available on iOS devices running iOS 9 or later, except for iPhone 4s, iPad 2 Wi-Fi+Cellular, iPad (3rd generation) Wi-Fi+Cellular, and iPad mini (1st generation) Wi-Fi+Cellular.
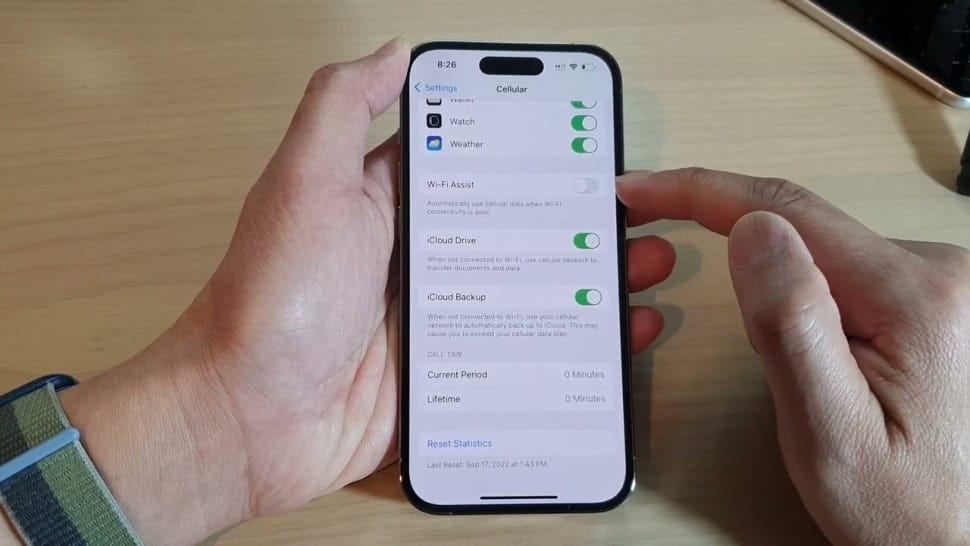
III. How does WiFi Assist work?
Wi-Fi Assist works by continuously monitoring your device’s WiFi connection quality. When it detects a weak or poorly performing WiFi signal, it automatically activates and switches to cellular data. This process happens in the background, without requiring any user intervention.
Key functionalities of Wi-Fi Assist include:
- Monitoring WiFi signal strength and performance
- Automatically switching to cellular data when necessary
- Balancing between WiFi and cellular usage for optimal performance
- Ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing internet activities
When Wi-Fi Assist activates, you’ll see the cellular data icon in the status bar of your device. This indicates that you’re now using cellular data instead of WiFi.
How does Wi-Fi Assist assess WiFi connection’s quality?
WiFi Assist employs sophisticated algorithms to assess the state of WiFi connection:
- Signal strength: weaker signals are typically below -70 dBm.
- Data transfer rates: The actual data transfer rates on the network
- Packet loss: The percentage of data packets that fail to reach their destination
- Latency: the delay between sending and receiving data.
When these parameters fall below certain thresholds, Wi-Fi Assist identifies the connection as weak or unreliable.
IV. Why turn on WiFi Assist – Benefits
There are 03 main benefits of Wi-Fi Assist:
- Improved internet connectivity, especially in large buildings, outdoor spaces, or when traveling abroad where WiFi signals can fluctuate dramatically.
- Smooth and uninterrupted browsing experience for users at all times
- Improved the performance of various applications, especially those that require a constant internet connection
By providing these benefits, Wi-Fi Assist transforms the mobile internet experience, making it reliable, efficient, and enjoyable.
VI. Why turn off Wi-Fi Assist – Drawbacks
While WiFi Assist is beneficial, there are some considerations about it that you may want to turn off:
- Increased data usage: Wi-Fi Assist may lead to higher cellular data consumption, which could be a concern for users with limited data plans.
- Potential for unexpected charges: If you’re unaware of Wi-Fi Assist using cellular data, you might face surprise charges or run out of data sooner than expected.
- Roaming considerations: When traveling internationally, be mindful of potential roaming fees if Wi-Fi Assist activates. But you can avoid roaming fees with a travel eSIM when you are abroad.
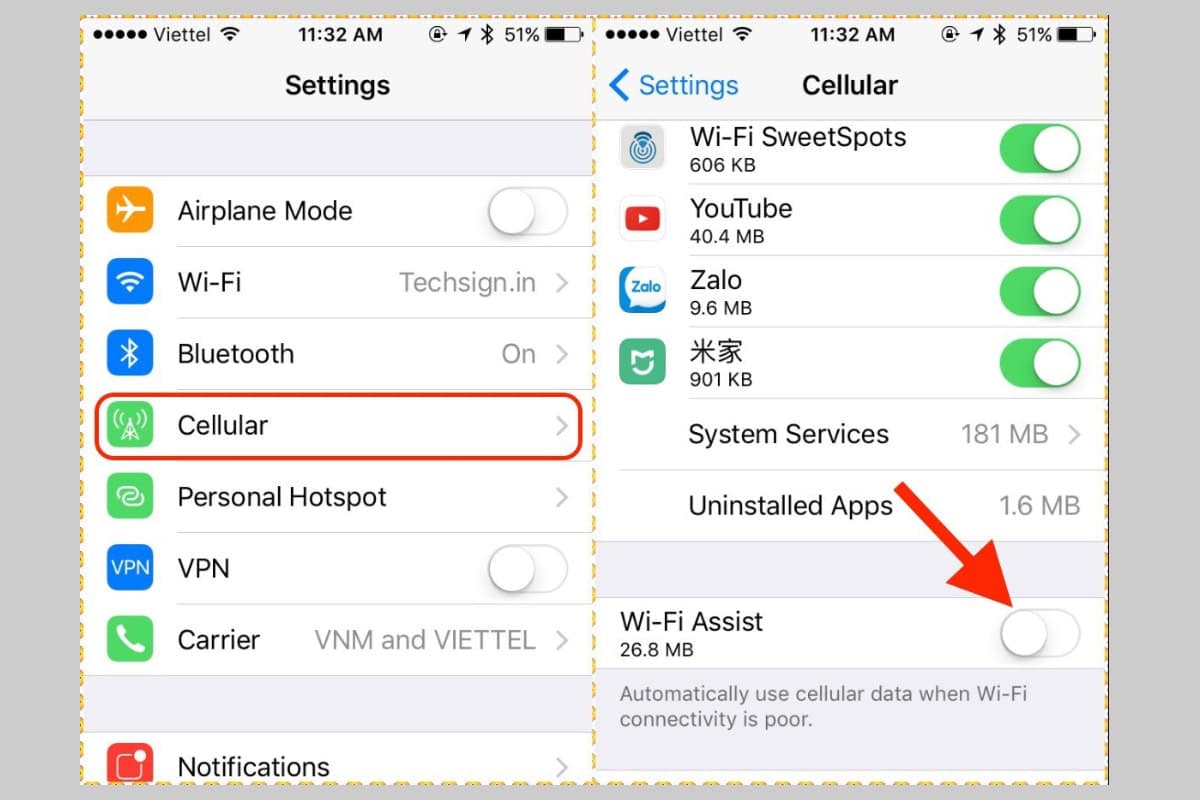
VII. How to turn Wi-Fi assist on and off?
- Go to Settings > Cellular / Mobile data (varied by region)
- Scroll down to find WiFi Assist
- Switch the toggle on or off depending on your preference.
VIII. How to troubleshoot common Wi-Fi Assist issues
Sometimes you may encounter issues related to Wi-Fi Assist. Here are common problems and their solutions:
1. WiFi assist not working
This is when your device does not switch to cellular data when WiFi is weak.
Solution:
- Check if your Wi-Fi Assist is enabled: Go to Settings > Cellular > WiFi Assist
- Confirm your device is running on iOS 9 or later
- Verify cellular data is on: Go to Settings > Cellular and ensure that the cellular data is enabled.
- Restart your device
2. Excessive Data Usage
You notice unexpectedly high cellular data consumption.
Solution:
- Monitor data usage: View data usage by app in the Settings and turn off cellular data for data-heavy apps
- Improve your WiFi network to reduce reliance on cellular data
3. Battery Drain
Your device’s battery life seems shorter when the feature WiFi Assist is enabled.
Solution:
- Check battery usage: Go to Settings > Battery to see which apps are consuming power
- Ensure all apps are up-to-date to optimize performance
- Adjust screen brightness to prevent increased battery usage
4. Unexpected Network Switching
Your device switches to cellular data even when WiFi seems strong.
Solution:
- Check if there are electronics or physical obstacles that can affect WiFi strength and remove them.
- Forget and rejoin WiFi network: Sometimes resetting the network connection can help
- Update your router firmware: Ensure your WiFi router is running the latest software
5. WiFi Assist Not Available
The WiFi Assist option is missing from settings.
Solution:
- Check device compatibility: Ensure your device supports Wi-Fi Assist
- Verify restrictions: Check if any restrictions are enabled in Settings > Screen Time > Content & Privacy Restrictions





