Traveling for a short trip, typically for 3- to 7-days, drastically changes the rules of connectivity. The traditional solutions like expensive carrier roaming or time-consuming local SIM buying are simply impractical when time time is precious. This is where eSIMs take the picture. The eSIM (embedded because it is a digital solution that solves the […]
What Is APN? How To Set It Up For iPhone + Android
Find out what is APN, its impact on connectivity and how to set it up for iPhone and Android step by step.
The term “APN” is commonly encountered when navigating your mobile device’s connectivity settings. A clear understanding about it can significantly enhance your internet experience. Here, we explain “what is APN“, and provide essential steps to configure APN settings on both iPhone and Android devices, ensuring you stay connected with optimal performance.
In this article
I. What Is APN?
APN (Access Point Name) is a gateway between a mobile device’s network and the public network. A mobile device to transmit data must be configured with an APN so as to present to the network carrier. The carrier will then identify this mobile device to determine if a private network is needed, choose the right security settings to use, etc.
To put it in simple words, imagine that your phone needs a special pass to access the Internet. That “pass” is called APN. It is like a bridge that connects your phone’s network to the wider Internet. For example, the APN of Viettel Vietnam is “v-internet”.
Features of APN:
Each mobile network carrier has its own APN. You normally do not have to change the APN settings because as soon as you put your SIM card in, your phone will automatically get the correct APN settings.
Why is APN important?
APN is important for your smartphone network functions because without it, your phone cannot create a suitable connection to the public network, and you will not be able to access the mobile data.
Note: If you buy a carrier-locked phone, you are probably not able to change APN settings on your phone.
II. How Many Types of APN Are There?
There are four different APN types, which are: Generic, SUPL, MMS, and WAP.
- Generic APN: this is the most basic and widely used type of APN. It is like the default settings for your phone’s internet connection.
- SUPL (Secure User plane location). This is specifically for location-based services. It helps your phone determine its location quickly and accurately using Assisted GPS (A-GPS). The apps like navigation, maps and locations-based services rely on this APN.
- MMS APN (Multimedia Messaging Service): As the name suggests, this APN is for sending and receiving multimedia messages (MMS) containing pictures, videos, and audio. It has specific settings to handle the larger data size of MMS compared to regular text messages. It’s a requirement on most MVNOs that use MMS.
- WAP APN (Wireless Application Protocol): This APN was used in older mobile devices for accessing WAP content, a simplified version of the web designed for mobile phones. With the advancement of mobile technology, WAP is rarely used today, and most modern phones use the generic APN for all internet access.
III. How Does APN Work?
An APN includes 02 parts: a network identifier and an operator identifier.
- The network identifier tells your phone which specific internet network it needs to connect to.
- The operator identifier network tells your phone which mobile network operator (MNO) or mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) is providing the connection.
When you use mobile data, your MNO or MVNO will check your APN to determine the following;
- Which IP address to assign to your phone
- Which network to connect your device to
- Which security measures to use
This opens the connection between your phone’s network carrier and the internet, thereby allowing you to stay online with your mobile data.
IV. Why Change APN Settings?
Normally, you do not need to change APN settings because it will be configured automatically by your carrier. However, you may need to change APN settings:
- when you insert a new SIM or eSIM which requires you to go to device settings to update APN.
- when you use a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO). These are small network carriers that lease the network access from the big major ones. Sometimes, they may require you to manually enter their APN settings, or
- when you experience connection issues or low internet speed
V. Understanding Terms of APN settings
After getting to the APN setting area in your phone, you will see a page with some terms that you need to understand:
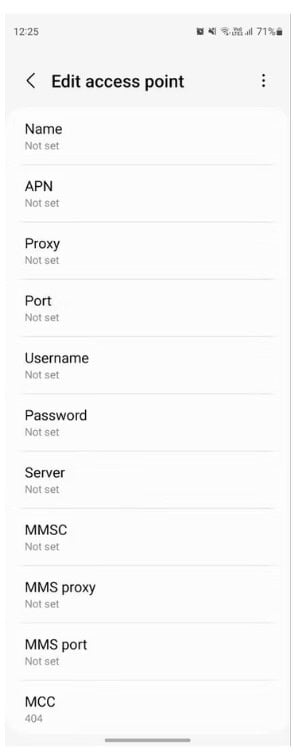
Name: the name of the mobile network carrier, such as T-Mobile or Verizon
APN: the most important setting. This is a special address that tells your phone how to connect to the internet network of your carrier. For example, T-Mobile users may need to enter “fast.t-mobile.com” here.
Proxy: some mobile carriers use this to set up a proxy between your mobile network and the internet. Imagine this is like a detour for your internet traffic. Most people leave this blank but you can use it to send your data through a different server.
MMSC: stands for Multimedia Messaging Service Center. It is a requirement for most MVNOs.
MCC and MNC: These codes help identify your mobile network operator, kind of like a country code and area code for your phone service.
VI. How To Find Your APN Settings
You can find the APN settings for your mobile carrier on its website or from the email sent from the carrier upon buying the SIM/eSIM.
For example, when you buy a SIM from T-Mobile, you will see this:
- Name: T-Mobile
- APN: fast.t-mobile.com (for LTE devices) or epc.tmobile.com (for non-LTE devices)
- Proxy: <Not set>
- Port: <Not set>
- Username: <Not set>
- Password: <Not set>
- Server: <Not set>
- MMSC: http://mms.msg.eng.t-mobile.com/mms/wapenc
- MMS proxy: <Not set>
- MMS port: <Not set>
- MMS protocol: WAP 2.0
- MCC: 310
- MNC: 260
- Authentication Type: <Not set>
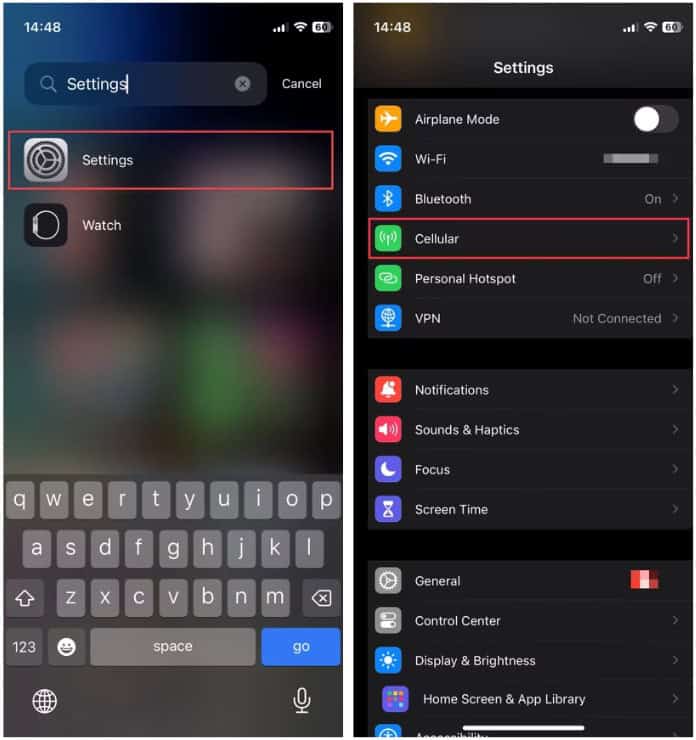
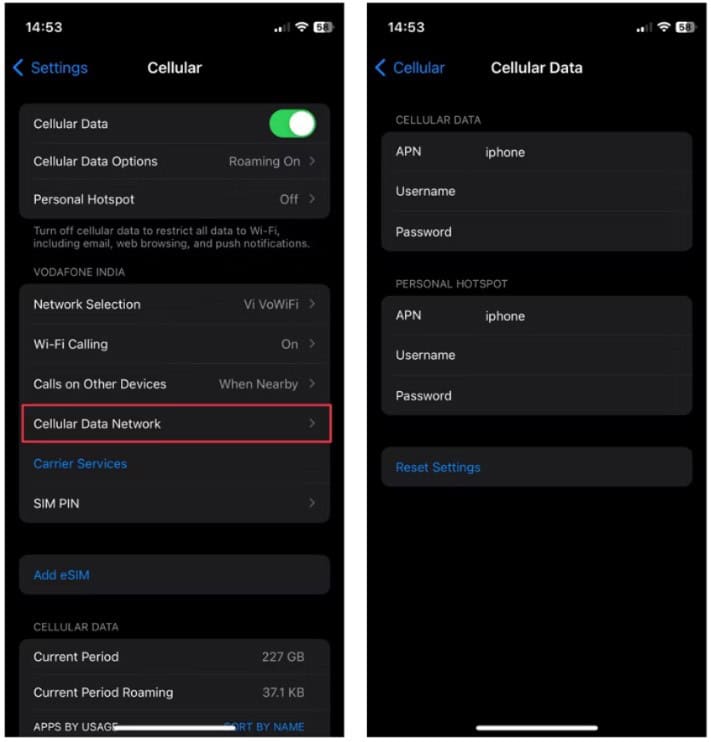
VII. How To Update APN Settings On iPhone
To get to APN settings in your iPhone, you need to take these steps:
- Go to Settings menu > Cellular / Mobile Data
- Choose your SIM/eSIM
- Select Cellular Network or Mobile Data Network
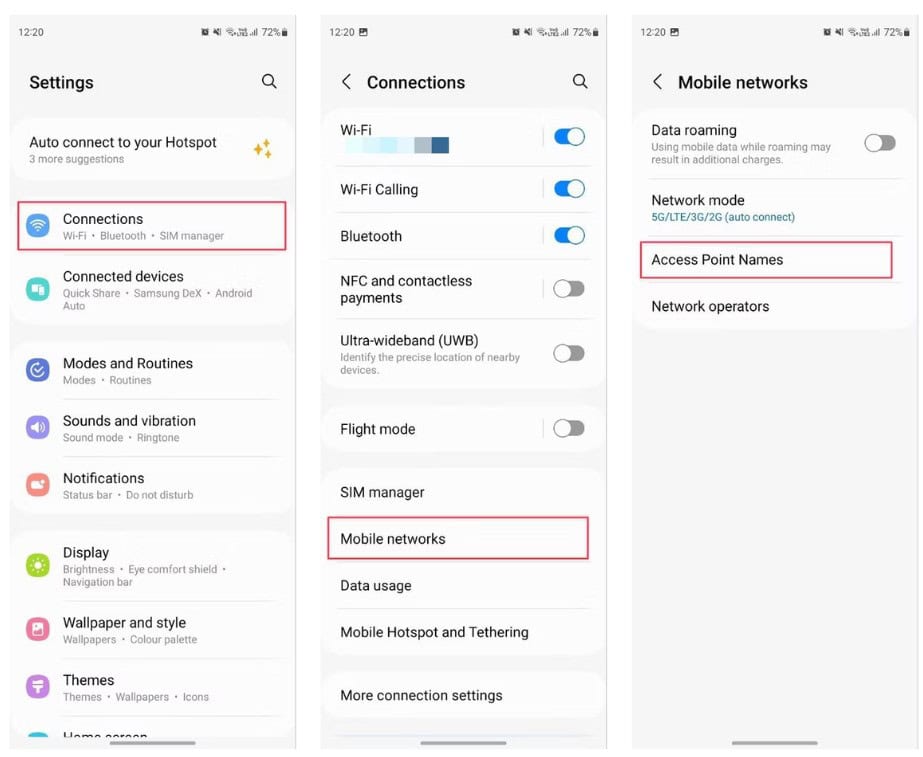
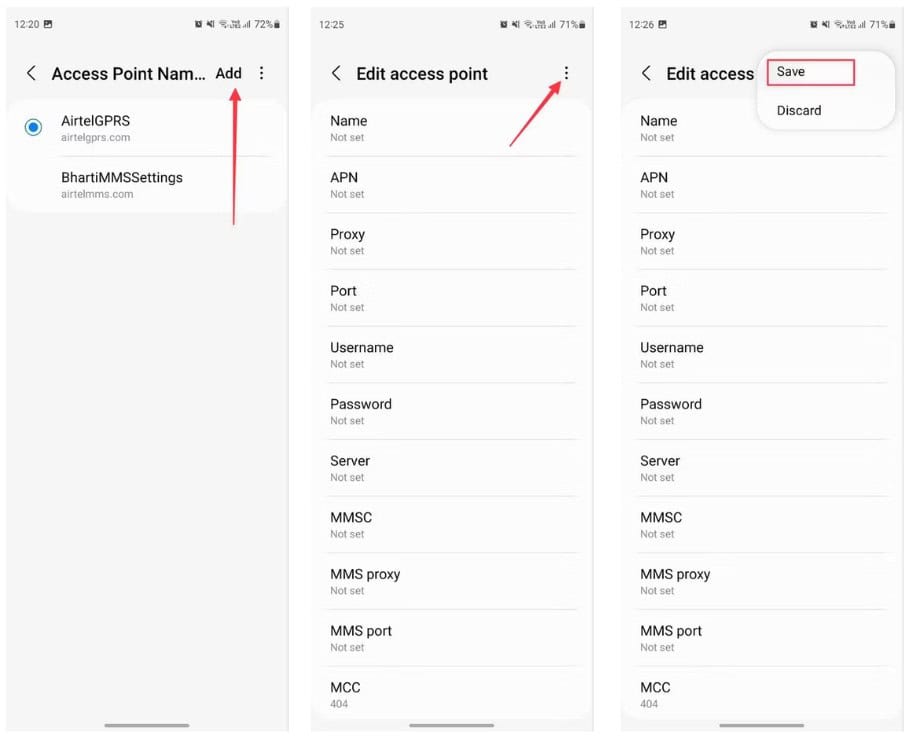
VIII. How to update APN settings on Android phones
The way to change APN settings on Android phones will be slightly different by specific device. Here, we use a Samsung device to instruct you:
- Go to Settings menu > Connections
- Choose Mobile Network Mobile Network
- Choose Access Point Names
- You will see the current APN settings, select the Add button to enter a new APN, then save the change
IX. FAQ about APN
Should APN be on or off?
APN settings should be on to ensure your mobile device can access the internet and other network services. Turning it off may result in connectivity issues.
What is the main use of APN in any mobile phone?
The main use of APN in mobile phones is to facilitate the connection to an internet service provider a cellular network. It acts as a gateway that allows the mobile device to access the internet as well as other data services given by the mobile carrier. The APN specifies the network path for all mobile data connectivity, thereby ensuring that users can send and receive data over the Internet, navigate the web, stream videos, and use apps that need a data connection.
Do I need to set up an APN for LTE?
Yes, you need to set up an APN for LTE service. The correct APN settings will ensure that your mobile device can access high-speed internet and other network services offered by your carrier. Most of the time, these settings are automatically configured on your device when you insert a SIM card. However, if there is connectivity issues or if you switch carrier, you need to set up APN manually.
How does Access Point Name (APN) affect a phone’s internet connection?
If the APN settings are not properly configured or incorrect, it can affect your phone’s ability to connect to the internet or use certain data services.
Is the APN on the SIM card?
Yes, APN settings are typically configured in advance on the SIM card by your mobile network carrier. When you insert a SIM card into your mobile device, it often automatically configures your mobile network settings, including the APN, to connect to the internet and other mobile network services.
What is APN on my network?
The Access Point Name (APN) is unique by carrier. You can find and edit APN settings under the Mobile Network or Cellular Network section in your device’s settings menu. In case you are not sure about the correct settings, you can find them on the website of your carrier or by contacting their customer service.