Traveling across Europe is exciting — with open borders and diverse cultures just a train ride apart. However, staying connected while hopping from France to Italy to the UK can easily become expensive and complicated if you rely on physical SIM cards or international roaming packages. Today, eSIM technology has revolutionized travel, allowing you to […]
What is Mobile Data Throttling? Causes, How to Test, Bypass It
Find out what mobile data throttling is, reasons behind, how to test and by pass it to get smoother internet experience.
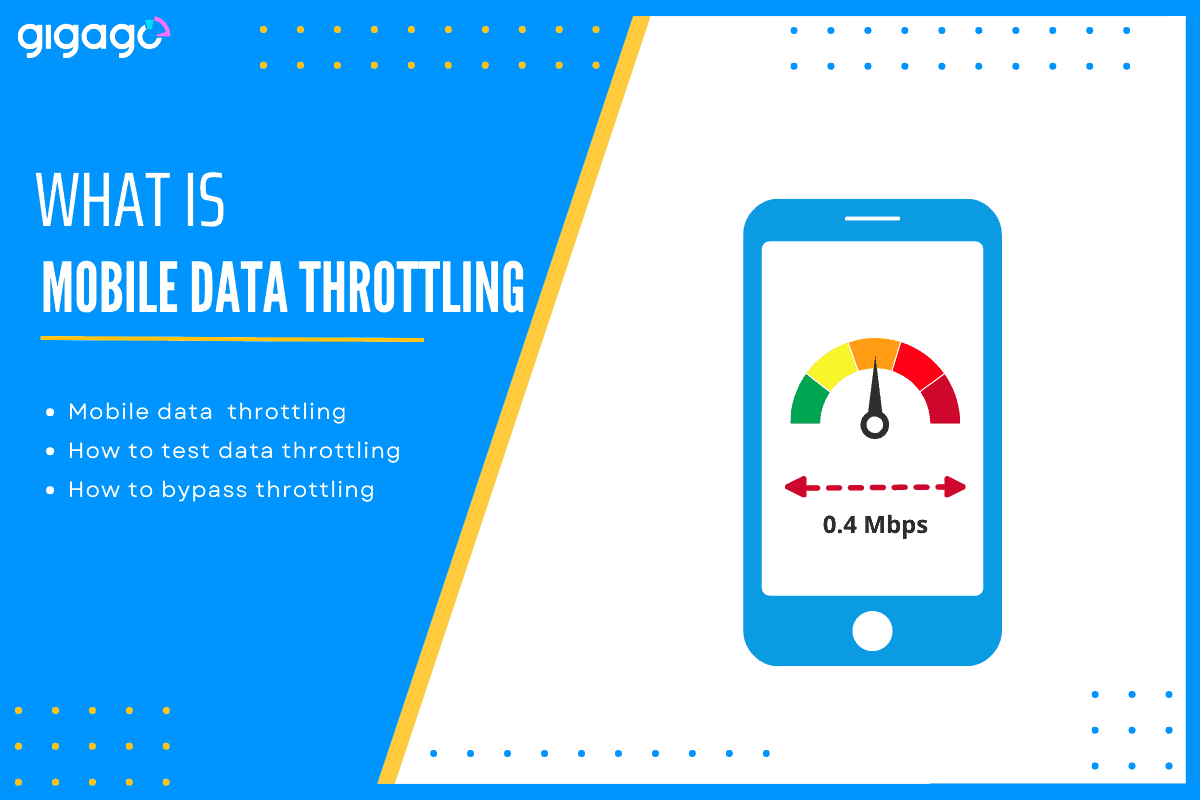
Mobile data throttling, also known as bandwidth throttling, is a frustrating problem that occurs when your Internet Service Provider (ISP) reduces your mobile internet speed. This typically happens when you need fast mobile internet but experience slow speeds instead.
This guide will explain everything about mobile data throttling, including what it is, why carriers do it, how to tell if you are being throttled, and how to bypass or minimize its impact.
In this article
I. What is mobile data throttling?
Mobile data throttling, or ISP throttling, is a process where your internet service provider or mobile carrier deliberately slows down your internet speed. This common practice often occurs when you have used up a certain amount of data or when the mobile network is congested.
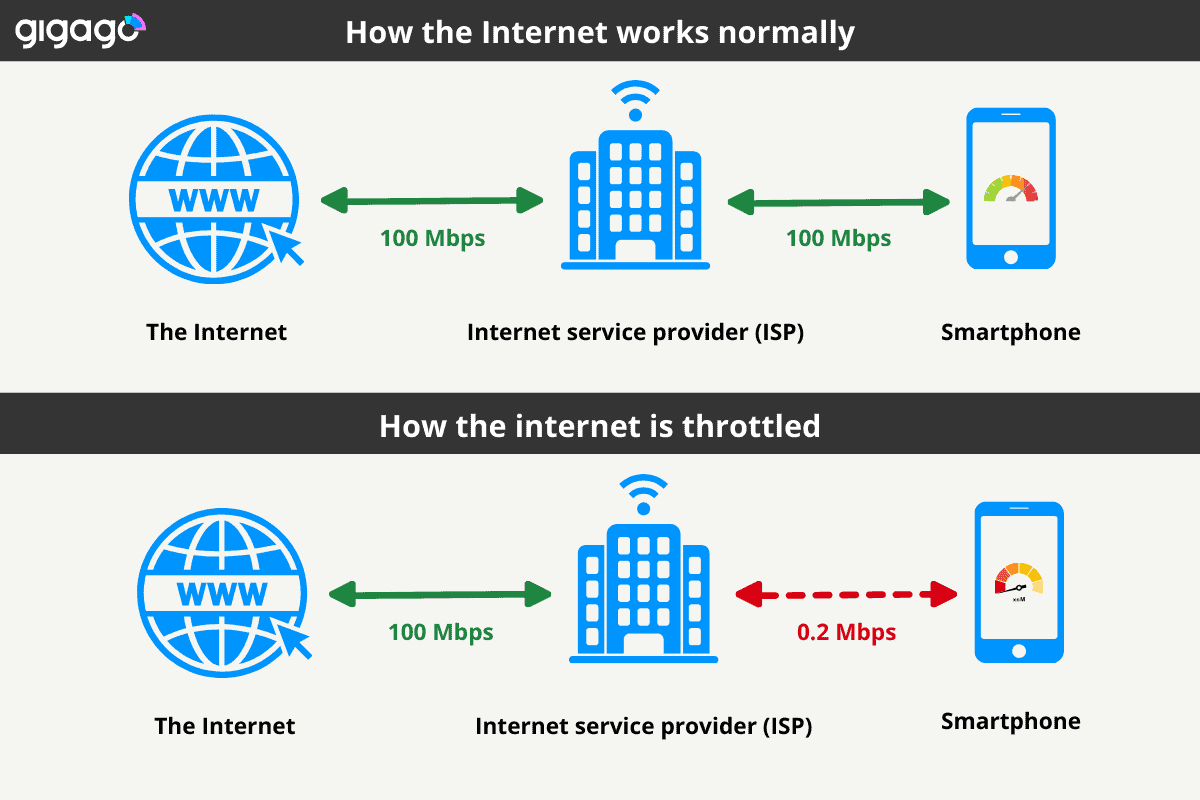
For example, consider the simple diagram illustrating data flow with and without throttling below.
Distinguish between throttling and de-prioritization
Data throttling and de-prioritization are two methods used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to manage network traffic, but they work in different ways and have distinct impacts on user experience. Here is a table summarizing the key differences between two concepts:
| Feature | Throttling | De-prioritization |
| Mechanism | Intentional speed reduction for all users | Lowering priority of specific traffic during congestion |
| Trigger | Data usage exceeding a limit, specific plan conditions | Network congestion |
| Impact | All users experience slower speeds | Affected users experience slower speeds only during congestion |
| Duration | Typically persistent until the next billing cycle or data limit reset | Temporary, occurring only during peak usage periods |
While both practices can be frustrating, deprirization can be less severe than throttling, because it only impacts users during specific conditions and allows for more nuanced traffic management.
II. How many types of data throttling are there?
Data throttling is available in different forms, depending on the ISP’s policies. Here are 05 common types:
1. Data cap throttling
Data cap throttling happens when you use up your data limit set by your internet service provider. This limit, called a “data cap”, is the maximum amount of high speed data that you are allowed to use. Once you exceed this limit, they may slow down your internet speed for the rest of the billing cycle.
For example, you streamed a lot of movies this month and hit your 20GB data cap. Now, for the rest of the month, websites load slower, and videos constantly buffer.
2. App-specific throttling
Application-specific throttling happens when your internet service provider or mobile network operator selectively slows down the internet speed for specific applications, not your entire connection. This often targets data-heavy apps like Netflix, Youtube, Spotify, etc.
For example, your Spotify streaming constantly buffers, even low quality, while browsing the web is fine. This can be your ISP throttling Spotify to save bandwidth.
3. Content-based throttling
This type of throttling involves slowing down access to specific types of content.
For example, you can browse websites normally, but downloading large files (games, software) is very slow. Your ISP may throttle these data-heavy activities.
4. User-based throttling
User-based throttling involves heavy users or who regularly exceed their data usage on the network. If you consistently use a lot of data, your ISP will throttle you to free up bandwidth for others.
For example, you are a gamer who regularly downloads huge updates. Your ISP notices this usage and throttles your connection during peak hours to prevent slowdowns for other users.
5. Time-based throttling
Time-based throttling happens at specific times of the day when the network is busiest.
For example, from 7 PM to 11 PM, your internet slows down significantly. This is likely time-based throttling because your ISP tries to manage peak-hour congestion.
III. Why do carriers throttle data? Common Causes
Mobile carriers have a lot of reasons to implement data throttling policies, but 03 most common are:
1. Network management and congestion control
When too many people use data at once (like streaming videos), the network may get congested. Carriers use throttling to slow down some connections, preventing a total internet crash and keeping things running for everyone.
2. Fair play for all users
Carriers want to ensure everyone gets a decent connection through their fair usage policies. So, they may throttle heavy data users to prevent them from hogging bandwidth and slowing things down.
3. Push you towards pricier plans
This is the controversial part. Sometimes, throttling is used to nudge you towards more expensive plans. Some plans are labelled as “unlimited” but there is a throttling threshold. Once you hit them, your internet speed will drop, tempting you to upgrade for a faster, uninterrupted experience.
IV. How to tell if your data is being throttled?
If you suspect that your internet speed is being throttled, here are 04 main ways to check for data throttling:
1. Recognize the symptoms
Know some common symptoms of throttled data:
- Significant slower speeds during particular times of day, particularly during peak hours.
- Consistent buffering or lagging when doing heavy-data activities like sending large files, playing online games or streaming videos.
- Video quality issues like sudden drops in resolution, pixelation and artifacting, or inability to select higher resolutions.
2. Track your data usage with data monitoring apps
You can use third-party apps like GlassWire or My Data Manager to track your data consumption in real time. These tools will show you how much data you are consuming, if you are nearing your data cap, which apps are using the most data, any trends in your usage.
3. Use speed test tools
Websites and apps like Speedtest.net or Fast.com can measure your internet speed, helping you pinpoint throttling.
First, you run a speed test when your internet seems normal to see your typical speeds.
Next, start a large download or stream a video, then run another speed test. If there is a significant drop, it indicates throttling.
Also, run speed tests at different times of the day, especially during peak hours. If you notice a consistent slowdown during these times, it may indicate throttling.
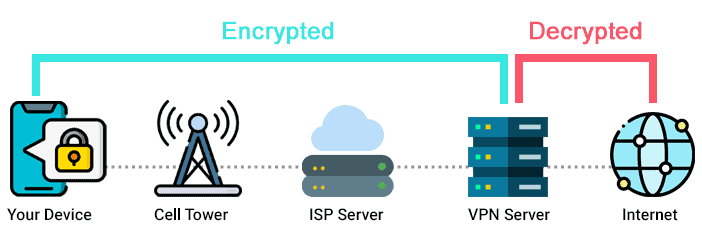
4. Test with a VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) will encrypt your internet traffic and probably bypass ISP throttling.
You can run a speed test without a VPN, then connect to the VPN and run the test again. If your speed improves while using a VPN, it indicates your ISP is throttling your internet connection.
By combining these methods, you can have evidence and confidently address any potential throttling issues with your ISP.
V. How to bypass mobile data throttling?
Encountering data throttling can be aggravating, but you can bypass or minimize its effects in 03 ways below:
1. Use a VPN service
As mentioned earlier, a VPN can help you bypass ISP throttling by masking your data traffic from your ISP.
A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it harder for your ISP to identify the types of data you are using.
Once your carrier cannot see what you are doing, they will be less likely throttled your connection based on specific activities like gaming or streaming.
Here are steps to using a VPN to bypass data throttling:
- Choose a reliable VPN with strong encryption and a wide range of server locations.
- Install the VPN app
- Connect to VPN server. It is better to choose the location close to your current location for better speed.
- Test your connection with a speed test or use the internet as normal to check if the internet speed has increased.
- Use the internet normally because your data is now encrypted.
Note: Choosing a reputable VPN service to avoid any potential overhead that may affect your speeds.
2. Switch to a different carrier
If you consistently cope with throttling and have limited options to bypass it, consider switching carriers. Throttling policies vary by network carriers. You should research and compare different carriers to find the plans that suit your data usage without excessive throttling impositions.
Tip: Check for consumer reviews and forums to have insights into experiences with carriers regarding throttling.
3. Upgrade your data plan
If you regularly hit the data cap and are throttled, upgrading your data plan with a higher data cap or even an unlimited data plan can solve the issue. While this option involves spending more money, it can provide a smoother internet experience.
You can also choose specialized plans designed for heavy users with prioritized traffic or higher data caps.
4. Monitor and reduce data usage
Proactively managing your data usage can significantly reduce throttling potentials.
You can limit background app refreshes, disable auto-play for videos, and connect to WiFi whenever possible. These actions can lead to a more enjoyable mobile internet experience.
5. Contact your ISP
Sometimes, simply contacting your carrier and asking about throttled issues can help. You can negotiate a better plan or find reasons why your internet connection is being throttled.
If you find the throttling is not justified, you can lodge a complaint with the related parties.
VI. Is Data Throttling Legal?
Yes, data throttling is generally legal if it is mentioned in the ISP’s terms of service.
In fact, the legality of data throttling varies by country and region. Some areas have strong net neutrality laws that generally restrict throttling, requiring ISPs to have valid justifications and apply it fairly.
Other regions have weaker regulations, giving carriers more freedom. Regardless of the specific laws, transparency is crucial. Carriers should be transparent about their throttling practices so customers can make informed choices.
VII. Data Throttling vs. Data Caps
Data throttling and data caps are often mentioned altogether, but they are distinct concepts.
Below we make a quick comparison table on data throttling vs Data caps:
| Feature | Data Throttling | Data Caps |
| How it Works | Reduces data transfer speeds, leading to buffering, lag. | Once the limit is exceeded, triggers consequences. |
| Triggers | Reaching a data cap Network congestion Specific app usage Time-based policies Upselling tactics | Reaching the defined data limit (e.g., 20GB) |
| Consequences | Slower internet speeds Poor video streaming quality Lag in online gaming Difficulty downloading/uploading files | Overage charges Throttled speeds Suspension of service (in some cases) |
| User Experience | Frustrating, especially for real-time applications. | Can be manageable if the cap is generous or usage is low. |
We can see that data caps define how much data you can use while data throttling involves how fast your internet is. Both can impact your internet experience, but in different ways. Recognizing the distinctions between the two practices can help users make educated decisions regarding their mobile plans.